“To be or not to be” is a famous quote from the Shakespearean play Hamlet. But sometimes in the course of learning English “to be” becomes quite problematic. This is because the verb “be” in English is what is known as an irregular verb - therefore it follows its own unique pattern. And yet it will be found in almost every piece of English writing or even the most basic of conversations. If this is leaving you pulling your hair out, fear not, this article will help in making verb conjugation in English as simple as possible.
What is English Verb Conjugation
Verb conjugation means modifying a verb according to the tense, gender, and aspect. A verb, or doing word, will change either in its ending or entirely depending on the subject, the tense, the number of doers, the mood, or the aspect. It provides detail as to who is doing the action, how many people are doing the action when the action is happening, and if it is still happening.
As the verb conjugation is the base of English grammar, you can learn it well in one month as long as you memorize the rules carefully.
Let’s take a look at the following examples:
Conjugation will always follow a pattern depending on the pronoun subject used and according to the tense:
The following pronouns will be found in every verb conjugation table:
They are: I, You, He/she/it, We, They
Note you may also come across “You Plural” but this is not very common and will not be focussed on much here. It should be noted that “You Plural” follows the same pattern as “You Singular”.
So in the case of the verb “Sing”
- I sing
- You sing
- He/She/It sings
- We sing
- They sing
“Sing” is an example of a verb that doesn’t change too much,
However, let’s take a look at the verb “be”, it changes vastly:
- I am
- You are
- He/She/It is
- We are
- They are
There is no magic formula here, it really is a case of memorizing. However, it is also worth highlighting here that “be” is the only English verb that changes 3 times in the present tense.
However let’s take a look at how the verb will change as the tense changes in the case of the verb - “go”
- I go to work - Present simple - I mean the action is happening at present
- I went to work yesterday - Past Progressive - the action has already taken place
- I will go to work on Monday - Future tense - this action will occur in the future
- I would go to work if I could - Conditional - There is an “if” that makes the action dependent on that condition
- I am going to work every day - Presently occurring and does occur regularly
- I have gone to work every day - Past perfect shows that the action has taken place already
Examples of Common Verbs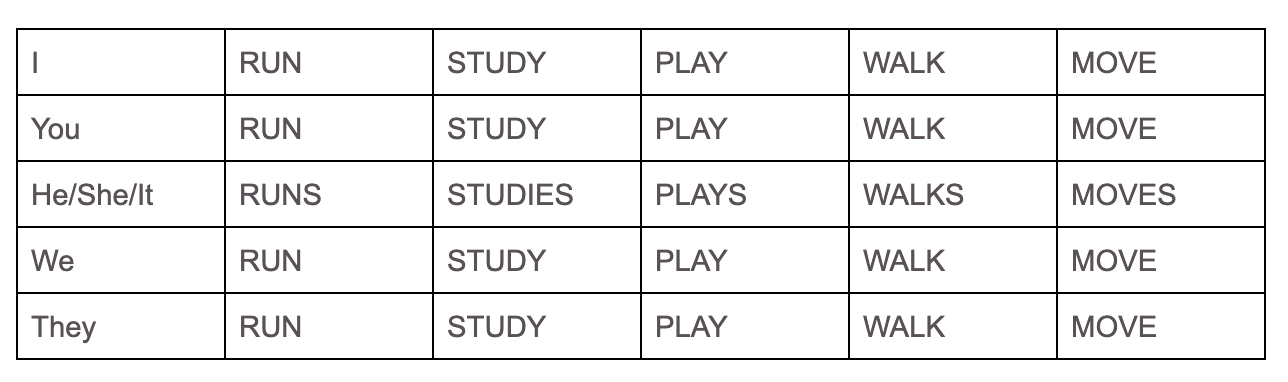
These verbs are what is known as “regular” verbs - this means that they follow a regular or consistent conjugation formula. As you can see in the examples above, the list is by no means exhaustive but merely serves to demonstrate a couple. These verbs can be identified as regular because they take the suffix “-ed” or “-d” in their past form.
Irregular Verbs
What then are Irregular verbs? They are quite simply verbs that do not follow a regular conjugation structure or pattern
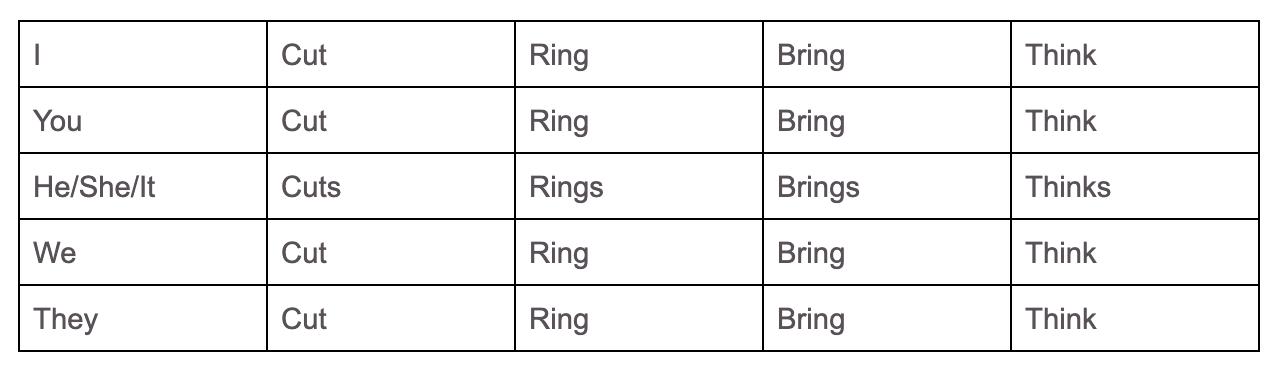
This seems very straightforward as it is only the Third Person singular that changes with an “s” added to the end.
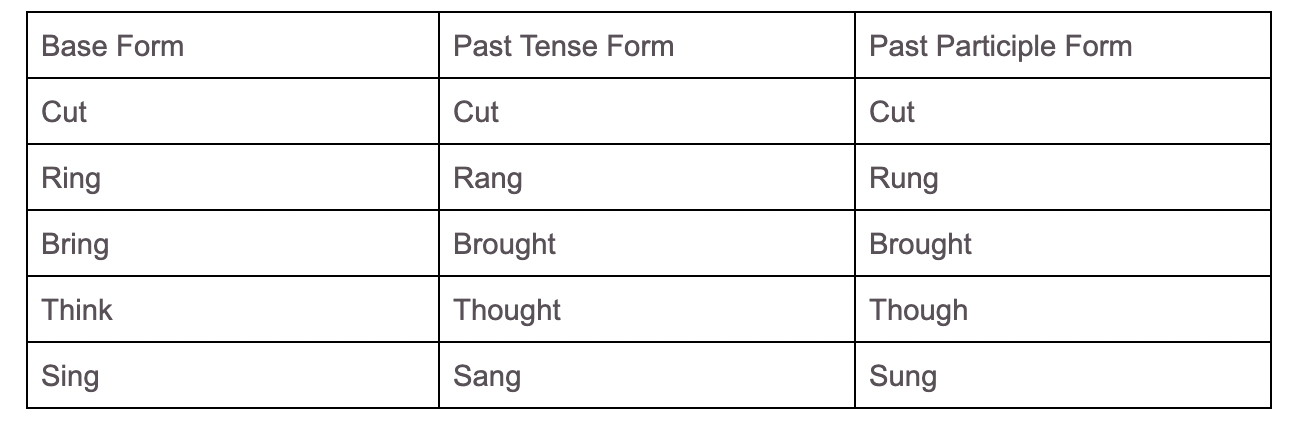
For example - this is just a small list. A good piece of advice to advance your English would be to learn these early on and learn them very well as they will stand you in good stead in the future.
A few more rules to note
The verb used shows to which degree an action is completed - for example,
- I am baking - Present Progressive (the action is happening at present)
- I bake - Present Simple (the action is something that happens occasionally, often but not at this present moment)
- I have baked - Present Perfect (the action is complete)
- Conjugating verbs is inextricably linked with time - it is used to show WHEN the action is taking place.
- As you can see in the following examples how the verb can be modified to show time and relation to the doer:
- She likes to dance but she dances alone.
- He didn’t dance with her, but we danced with her later.
- They left dancing to the younger folks but said they will dance again when a better song comes on.
Tenses
English becomes complicated when you note that there are up to 16 different tenses to indicate the time in which the action happened/will happen but do not let that intimidate you. The tenses can be simply broken down into 5 groups
- Present, Past, Future, Conditional and Perfect
- Past tense conjugation:
Simple: She went to the supermarket
Past progressive: She was going to the supermarket
Present tense conjugation:
Simple present: I buy apples at the supermarket
Present progressive: I am buying apples at the supermarket
- Future tense conjugations:
Future simple: He is going to have dinner at 7 o'clock
Future perfect: Will they have dinner at 7 o'clock?
Future progressive: They will have dinner at 7 o’clock
- Perfect tense
Present perfect simple: He has spoken about it
Present perfect progressive: He has been speaking about it
Past perfect progressive: He had been speaking about it
Past perfect simple: He had spoken about it
- Conditional tense conjugations
Conditional simple: We would consider your proposal
Conditional perfect: We would have considered your proposal
Conditional progressive: We would be considering your proposal
Conditional perfect progressive: We would have been considering your proposal
Conclusion
A few good pointers:
As you can see in the above examples most verbs in English are connected through the use of “helping” verbs such as would, will, had, did or did not.
There are some exceptions in verbs and it would be wise to learn the exceptions first.
One way some students learn is to recite tables of how the verbs change and learn lists of irregular verbs. Some students record this table and listen to it on the way to work or school. This is only one way to go - you need to find a method that suits you. Oftentimes it is more helpful to read widely and listen to podcasts or the news where you hear the words spoken naturally and over time start to pick the correct tense up through hearing.
What works for you to learn verb conjugation? Comment below I would love to hear some suggestions. And if you want to learn English well, you can book English lessons with me. I’m a native English tutor and can help you study English online.







